Pronouns in English: Definition, Types, and Examples
Last updated: Jul 28, 2025Pronouns are one of the most useful parts of speech in the English language. They help us avoid redundancy, improve sentence flow, and make communication more efficient. While their role may seem subtle, pronouns are essential tools in both spoken and written language. In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at what pronouns are, the different types of pronouns, and how they work to simplify our communication.

Table of Contents
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun (person, place, thing, or idea) to avoid repetition. By substituting a noun with a pronoun, we can make sentences shorter and more natural-sounding, which is especially important for keeping our conversations and writing engaging.
For instance, instead of saying:
"John is going to the store. John will buy some bread." We can replace the second "John" with a pronoun: "John is going to the store. He will buy some bread." The pronoun "He" substitutes the noun "John," making the sentence more concise and easier to read.
Also read: How to introduce yourself in English?
What Are the Types of Pronouns?
As the use of pronouns is very diverse and common, the English language has several types of these pronouns. All of them can be used in different contexts. There are 10 types of pronouns in English language. They are:
1. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns are used to connect a clause or phrase to a noun or pronoun, adding more detail or clarification. Some of the most common relative pronouns include words like 'who,' 'whom,' 'whose,' 'which,' and 'that'.
Examples:
- The woman who called is my aunt.
- The book that you gave me is excellent.
- The artist whose painting won is here.
2. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and object refer to the same person, and they always end in -self or -selves.
Examples:
- He hurt himself while skating.
- I made the cake myself.
- They blamed themselves for the loss.
3. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to particular people or things, helping to specify which one is being referred to. Words like this, that, these, and those are commonly used as demonstrative pronouns.
Examples:
- This is my favorite mug.
- Those are not yours.
- I don’t like that.
4. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership or possession, showing that something belongs to someone. They include words such as mine, yours, his, hers, theirs, and ours.
Examples:
- That car is mine.
- Is this jacket yours?
- Ours is the blue one.
5. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things, and they change depending on their role in the sentence. They include subject forms like I, you, and he, as well as object forms such as me, you, and him.
Examples:
- I am learning French.
- She told me the news.
- They are arriving soon.
6. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things, often used when the exact identity is unknown or unimportant. Words like someone, anyone, nothing, all, and each are common examples of indefinite pronouns.
Examples:
- Someone left their phone.
- Everything is ready.
- None of the students were late.
7. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions and help gather specific information. Common interrogative pronouns include who, whom, whose, what, and which.
Examples:
- Who is at the door?
- What do you want?
- Which one is yours?
8. Emphatic Pronouns
Emphatic pronouns are used to emphasize or stress the subject of a sentence. While they look similar to reflexive pronouns, their main purpose is to add emphasis, not reflect the subject.
Examples:
- I myself cleaned the room.
- The president himself signed the letter.
- She herself confirmed the news.
9. Distributive Pronouns
Distributive pronouns refer to members of a group one at a time, emphasizing individual items or people. Common distributive pronouns include each, either, and neither.
Examples:
- Each of them was given a prize.
- You can choose either of the books.
- Neither was correct.
10. Reciprocal Pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns indicate mutual actions or relationships between two or more people or things. The most commonly used reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
Examples:
- They respect each other.
- The classmates helped one another with homework.
- We should support each other.
These are the different types of pronoun. You must try using them in various sentences to learn them and their difference. For this, you can also refer to the pronouns chart in the section below and know where to use which pronoun.
Also read: Difficult words in English with meaning
English Pronouns Chart
There are more than 100 pronouns in English language that you can use. As noted before, these are used to replace nouns in a sentence. These also make up a huge fraction of daily use English words. However, their usage differs from 1st person to 2nd and 3rd person. Also, these vary as per singular and plural nouns. Below is a table to explain this usage in detail:
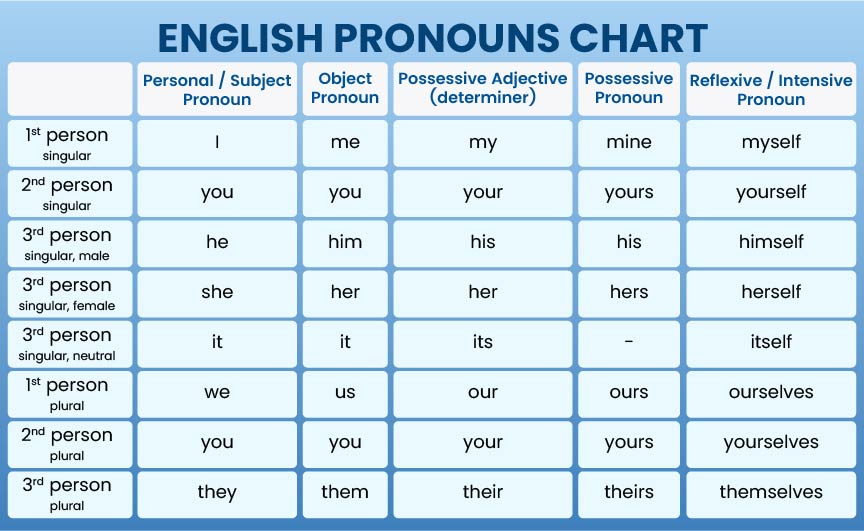
Hopefully, the table above helped you understand the usage of different pronouns in all contexts. For more clarity, we have also given some pronoun examples in the section below.
Also read: Proverbs in English
Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
Now that you know about pronoun definition and types, let us focus on some examples to get a better idea of their usage:
- It was a good time when I used to be on good terms with you. (Relative pronoun).
- His wife is Emily’s best friend. (Possessive pronoun).
- I wish everyone could experience a good new year. (Indefinite pronoun).
- Did he do it himself? (Intensive pronoun).
- She is the one worthy of all your appreciation. (Personal pronoun).
- I wish I could bring my mother with me. (Possessive pronoun).
- They help each other in learning. (Reciprocal pronoun).
- It is nice to have the entire house to oneself. (Reflexive pronoun).
- Whose is this jacket? (Interrogative pronoun).
- This is an apple and those are the oranges. (Demonstrative pronoun).
These are pronoun examples of each type. Now you must be aware that there are differences between nouns and pronouns. If not, don’t worry! The next section will elaborate on these differences in detail.
Also Read: Degrees of Comparison
Difference Between Pronouns and Nouns
Many people get confused with the terms pronouns and nouns. They often seem same but are slightly different. Apart from the major difference in their meanings, here is the detailed difference between pronouns and nouns:
| Pronouns | Nouns |
|---|---|
| Pronouns are words that are used in place of nouns. | A noun can be a name of a persona, place, animal, thing, or even idea. |
| There are more than 100 pronouns in the English language. | They are one of the major word classes. This means that the English vocabulary has a lot of words and a most of them are categorized as nouns, then verbs, adjectives, and so on. |
| There are 10 types of pronouns: indefinite, reflective, demonstrative pronouns, etc. | There are 12 types of nouns: proper noun, common noun, material noun, plural and singular noun, etc. |
| For example, pronouns can look like: she, they, them, it, her, his, oneself, themselves, mine, yourself, and so on. | Examples of nouns are: Ronny, hut, affinity, lake, desert, and so on. |
Apart from these important differences between pronouns and nouns, you must also know how they are different from determiners. The next section will explain how determiners and pronouns vary with examples.
Difference Between Pronouns and Determiners
After the difference between pronouns and nouns, there is another term called determiners. Many confuse them with pronouns. Thus, the table below will elaborate on the differences between pronouns and determiners.
| Pronouns | Determiners |
|---|---|
| Pronouns are used in place of nouns. | Determiners are used before nouns. |
| There are over 100 pronouns in the English language that you use daily. | There are 4 types of determiners: 1. Articles: a, an, the 2. Demonstratives Possessives 3. Quantifiers 4. Numbers |
| For example, pronouns can look like: she, they, them, it, her, his, oneself, themselves, mine, yourself, and so on. | For example, a, an, the, this, that, your, his, her, some, many, one, two, and so on. |
To sum up, pronouns are one of the most important parts of speech. So much so that you use it almost daily while communicating in the English language. This blog showed the correct usage of every type of pronoun before supporting verbs. It is essential to learn if you wish to speak English fluently and correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence, allowing us to avoid repetition. For example, instead of saying “John is my friend. John is very kind,” we can say, “John is my friend. He is very kind,” where “he” replaces the noun “John.
2. What are the Types of pronouns?
Here are the main types of pronouns in English:
- Relative Pronouns
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Possessive Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Interrogative Pronouns
- Emphatic pronouns
- Distributive Pronouns
- Reciprocal Pronouns
- Intensive Pronoun
2. What are some examples of pronouns in sentences?
Here are a few simple examples of pronouns used in everyday sentences:
- She went to the market to buy some vegetables.
- I can't believe this gift is mine!
- John looked at himself in the mirror before the interview.
- Those are the shoes I was talking about.
- Who left the door open?
- The book that you lent me was really interesting.
- Someone called while you were out.
- We’ll take care of it for you.
- Is that coffee yours?
- They helped themselves to the snacks.
3. What’s the Difference between a Noun and a Pronoun?
A noun is the name of a person, animal, place, or thing. Pronouns are words that can be used in place of these names. She, he, they, someone, mine, yourself are all pronouns.
4. Can pronouns be used in place of both people and objects?
Yes! Pronouns can replace both people and objects. For example, “She (a person) went to the store,” and “It (an object) is on the table.
5. Can "they" be used as a singular pronoun?
Yes, “they” can be used as a singular pronoun when referring to a person whose gender is unknown or when someone prefers “they” as their pronoun. Example: If someone says, “Alex is coming over later, I hope they bring dessert,” the word “they” refers to Alex in a gender-neutral way.
0 comments
Improve your English faster with expert online coaching
Learn EnglishWe are available in :
BangaloreAhmedabadJaipurHyderabadKeralaPuneChandigarhMumbaiGurgaonChennaiKolkataTrivandrumNoidaKochiCalicutKottayamKollamThrissurIndoreUdaipurdisclaimer:logos and other registered trademarks of universities used on this platform are held by their respective owners. Gradding does not claim ownership or association on them, and their use is purely for informational and illustrative purposes.








