German Verb Conjugation for Present, Past & Future Tenses
Last updated: May 19, 2025Want to speak German with confidence? But afraid you’ll make grammatical mistakes? Don’t worry, the first step toward speaking fluent German is understanding German verb conjugation. This is the way a verb changes its form to match the subject, the tense, the mood, and even the voice.
If you find this a bit difficult to understand, don’t worry. Our blog below will tell you everything about conjugating verbs in German, along with a German Verb Conjugation Chart for you to understand it better. Read on!

Table of Contents
What is German Verb Conjugation?
First things first, what is a German verb conjugation? What does it involve? And why are they important?
The verb conjugation in German is a process of changing the form of the verb to indicate or express different grammatical features like mood, tense, voice, person, and number. This is generally done by adding prefixes or auxiliary verbs, as well as stem modification.
In German, the verbs need to agree with the subject in person (I, you, he/she/it, we) and number (singular or plural), just like in English. For example, the verb “Gehen”, which means “to go” in English, turns into “Ging” when we conjugate it into the past tense.
When we learn German, understanding how to conjugate verbs is an important aspect, as it helps in forming correct sentences. In addition to that, it also helps in expressing who is acting accurately.
Explore Top Courses to Study in Germany
Options of a Wide Variety of Courses in germany


Classes of German Verbs
The verbs in German are primarily classified into two different forms: Regular and Irregular verbs. This is primarily based on how they change or do not change their form during verb conjugation in German. Let’s first understand what these two classes are and what role they play.
- Regular Verbs: These are also known as Weak verbs, and when we conjugate them, they follow a consistent and predictable pattern.
- Irregular Verbs: Also known as strong verbs, these verbs follow their path and change their stem vowels as per the tense.
Now let’s see how the regular and irregular verb conjugation works in different tenses.
Also Read: German pronouns
How to Conjugate German Verbs?
So, how to conjugate German verbs? You can do this in several different ways, however, there are general parts of the process which usually remain the same. This is especially true when it comes to conjugating regular verbs. Below are the three basic steps that you can follow for the conjugation of a regular verb.
1. Begin with the Infinitive: The infinitive is the base form of the Verb, something you will find in the dictionary as it is. For example, the verb for “to play” in German is spielen.
2. Find the Verb Stem: Once you find the infinitive, you can then easily find the verb stem by removing its endings. Generally, most regular verbs end in -en, -eln, or -ern. However:
- If the verbs end in -en like spielen, just take off -en to get the stem: spiel-.
- If the verbs end in -eln or -ern, only remove the –n. For example, segeln (to sail) becomes segel- and wandern (to hike) becomes wander-.
3. Add the Correct Ending: After you are done with the first two steps, attach the right ending to the stem. This is based on who is doing the action (I, you, we, etc.) and when it’s happening (present or past).
For example: In the present tense, “Ich lese” = “I read” (right now)
- Ich = "I"
- lesen = "to read" (the infinitive form)
- lese = the ich (I) form of lesen in the present tense
So: Ich lese ein Buch. = I am reading a book.
German Verb Conjugation in Present Tense
A widely used tense in German is the present tense. And just like English, you can use this tense to talk about things that are either happening in the present or will happen in the near future.
Here, we call it the simple tense because you will only need one verb to say what you mean. However, there are some regular patterns that you’ll notice with present-tense verbs, which you will find below:
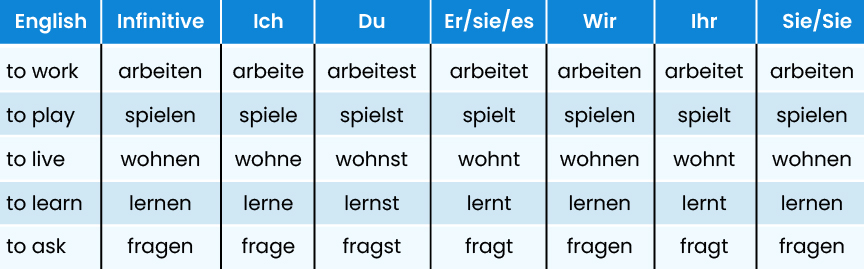
Regular -en Verbs
Below are the endings for regular verb conjugation along with examples:
- The ich (I) form usually ends in -e
- The du (you, informal) form usually ends in -st
- The er/sie/es (he/she/it) and ihr (you all) forms usually end in -t
- The wir, sie (they), and Sie (you, formal) forms usually stay the same as the verb's basic form (called the infinitive)
For example:
Regular Verbs Ending in -eln
In German, the verbs that end in –eln have a small variation in the ich form (I-form) in the present tense. Here, instead of adding -e to the stem, you can drop the -el and replace it with –le. So, for klingeln (to ring), you can use both ich klingele or ich klingle, which is the shortened version.
Hence, the verb conjugation in German for –eln would be:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| ich | klingele / klingle |
| du | klingelst |
| er/sie/es | klingelt |
| wir | klingeln |
| ihr | klingelt |
| sie/Sie | klingeln |
Regular Verbs Ending in –ern
Lastly, in the present tense, the verbs that end with –ern, follow a regular pattern. The German verb conjugation for these can easily be done by removing the final -n from the infinitive to form the stem, then adding the usual present tense endings.
Hence, the verb conjugation for ändern (to change) would be:
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| ich | ändere |
| du | änderst |
| er/sie/es | ändert |
| wir | ändern |
| ihr | ändert |
| sie/Sie | ändern |
Conjugating Irregular Verbs in Present Tense
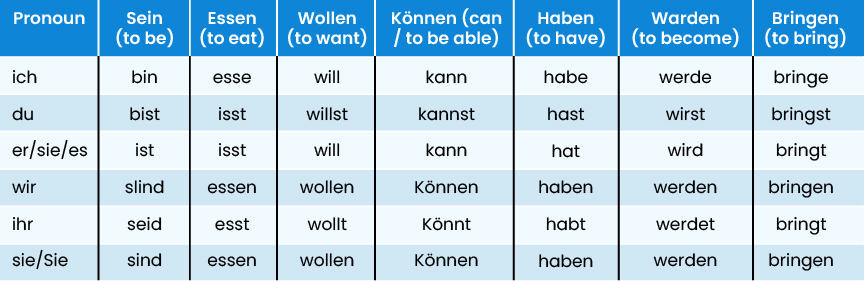
Just like the regular verbs, there is also an irregular verb conjugation process. Some of the most common and useful verbs are:
- Sein (to be): This is completely irregular and has no consistent stem.
- Essen (to eat): This changes its stem to iss- in du and er/sie/es.
- Wollen (to want): Here we use will- for ich, du, er/sie/es and woll- elsewhere.
- Können (to be able to / can): können shifts stems between kann-, konn-, and könn-.
- Haben (to have) and werden (to become): They also have irregular forms.
Additionally, while most irregular German verb conjugation follow a similar pattern, some have their unique changes to their stem. These are generally the strong verbs, and they have vowel changes or irregular changes. Below is a German verb conjugation Chart on how irregular verbs conjugate in the present tense.
Also Read: German Adjectives
German Verb Conjugation in Past Tense
Now let’s see how to conjugate German verbs? in the past tense. In German, the Präteritum is the simple past tense and is called “simple” because it only uses one verb. In the regular verbs, all the past tense endings have a T in them. Additionally, the ich and er/sie/es forms are the same, and the wir and Sie forms are the same, too.
However, the verb stems for wir and Sie are more common in their infinitive forms. Let’s check the German verb conjugation in the past tense.
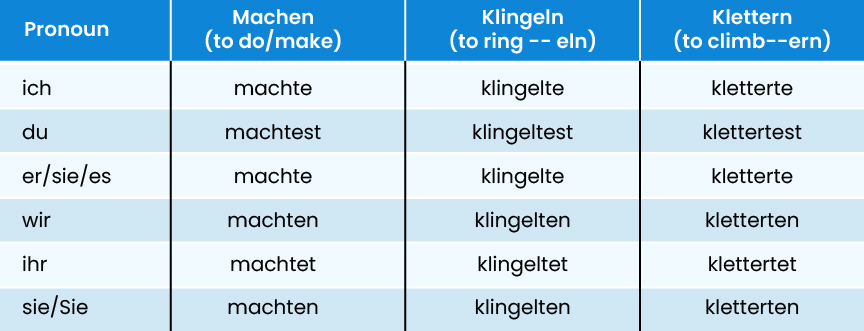
Regular Verb Conjugation in Past Tense
In the regular verb conjugation, the endings follow a predictable pattern. However, for -eln and -ern verbs, the endings adjust slightly, but they mostly stay regular.
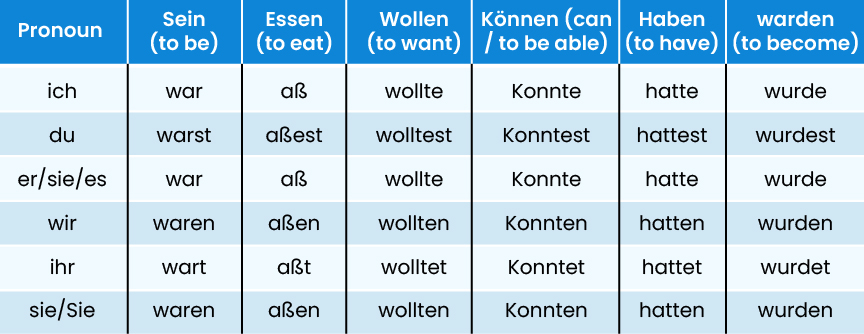
Irregular Verb Conjugation in Past Tense
The Irregular verb conjugation in the past tense doesn’t generally follow a regular pattern. However, even if the sein has irregular forms in the present, its past is more regular-looking.
Mixed Verb Conjugation in Past Tense
Lastly, in the past tense, there are some verbs like bringen which change their stem a lot. For example, bringen becomes brach-. The same happens with denken (dach-) and kennen (kann-).
However, do keep in mind that even though the stems change, these mixed verbs often use the same past-tense endings as regular verbs.
| Subject | Conjugation |
|---|---|
| ich | dachte |
| du | dachtest |
| er/sie/es | dachte |
| wir | dachten |
| ihr | dachtet |
| sie/Sie | dachten |
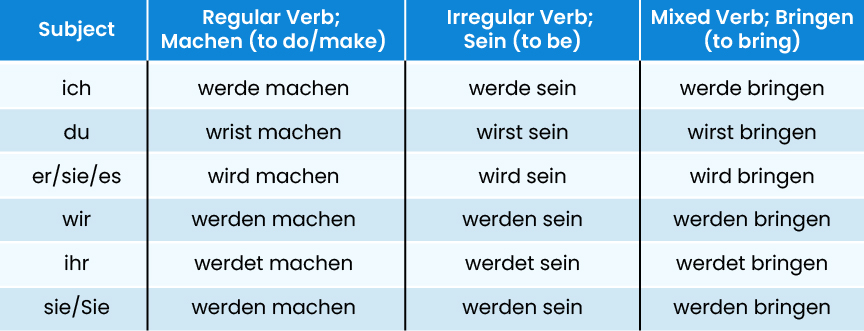
German Verb Conjugation in Future Tense
Lastly, the German verb conjugation in the future tense. In German, the future tense is not called a “simple” tense. However, it is relatively easier as compared to the past or present tenses. This is mainly because you need two things to talk about the future in German. These are:
- The present tense of the verb werden
- The infinitive (basic form) of the verb you want to use
Do keep in mind that these rules are generally followed by all types of verbs: regular, irregular, and mixed.
Also Read: Personal pronouns
Conclusion
And there you have it, everything about the German verb conjugation along with German verb conjugation chart. Even though they play a big role in your German language learning journey, understanding them can be quite complex. But don’t worry, you can take expert help from Gradding.com. There, you will get tailored German online coaching along with extensive resources, which will help you improve your German proficiency. Connect with our experts today!
Main Reasons Why you should Study in Germany
FAQs
How Do You Conjugate a Verb in German?
You can conjugate a German verb by finding the verb stem and then adding specific endings which will match the subject. For example, ich for "I", du for "you", and so on and the tense. Additionally, keep in mind that regular verbs follow consistent patterns, while irregular verbs may change the stem as well.
What Are The 8 Irregular Verbs in German?
Some of the most common irregular verbs in German follow standard conjugation rules and often have changes in their stem. These include:
- sein (to be)
- haben (to have)
- werden (to become)
- gehen (to go)
- kommen (to come)
- sehen (to see)
- nehmen (to take)
- geben (to give)
How Many German Conjugations Are There?
In every tense, the German verbs are generally conjugated for six grammatical persons, which are ich, du, er/sie/es, wir, ihr, sie/Sie). Additionally, there are different conjugation patterns as well for regular, irregular, and modal verbs.
Is German Verb Conjugation Hard?
Even though the German verb conjugation might feel a bit challenging at first because of the different endings, irregular forms, and stem changes. But once you learn the patterns and practice regularly, it becomes much more manageable and intuitive.
0 comments
Looking for Expert Guidance? Contact Us Today!
Call NowWe are available in :
BangaloreAhmedabadJaipurHyderabadKeralaPuneChandigarhMumbaiGurgaonChennaiKolkataTrivandrumNoidaKochiCalicutKottayamKollamThrissurIndoreUdaipurdisclaimer:logos and other registered trademarks of universities used on this platform are held by their respective owners. Gradding does not claim ownership or association on them, and their use is purely for informational and illustrative purposes.








