IELTS Listening Plan and Diagram Labelling: Samples, Expert Tips
Last updated: Jan 27, 2026Remember solving puzzles, joining dots, and finding hidden paths in childhood! The same level of curiosity returns in IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling questions, which once felt like games, now demand precision. Many students find this section tricky, but working on orientation, location/directional vocabulary, and real sample tests helps you to turn every question into an opportunity to boost your overall band score in the IELTS listening module.

Table of Contents
Introduction to IELTS Listening Plan/ Diagram Labelling
The IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling questions ideally appear in sections 1, 2 or 3 with 5 to 10 questions in each task. Plan and diagram labelling task differs from other types of listening questions as the answers are not directly stated in the audio. With quick thinking and precise vocabulary, all you need to do is interpret layouts, track orientation and directional clues. However, both the diagram and the IELTS listening plan labelling task may seem similar, but require different approaches.
1. Plan: Focuses on rooms, buildings, or areas from a top-down layout and spatial vocabulary.
2. Diagram Labelling: Involves process, machinery or pathways.

 Access Listening Mock Test
Access Listening Mock Test Key Component of IELTS Plan/Diagram Labelling Questions
Many of the students find these IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling one of the easiest types of questions to attempt, as the graphic comprises lots of clues, such as:
1. Orientation: Gives you the total layout or context of the IELTS listening diagram labelling, or plan. This gives the right flow to follow.
2. Starting/Ending Point: Recognise the starting point or beginning/end of the sequence. These points help you follow the process logically and ensure each step or location is labelled correctly.
3. Keywords: Are the phrases or words in the audio that match or hint at labels in the diagram.
IELTS Listening Plan and Diagram Labelling Samples
This is how thediagram and IELTS listening plan labelling sample will appear on your question paper. Take a look:
Sample 1
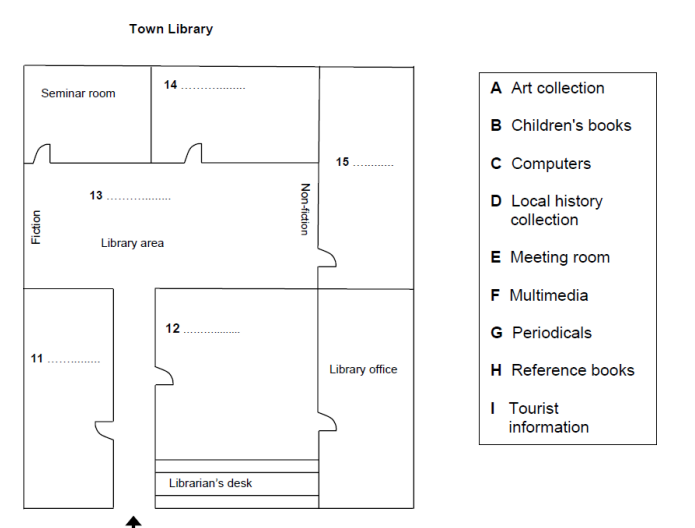
Sample 1 covers an IELTS listening plan type of question, in which you will hear the librarian of a new town library talking to a group of people who are visiting the same library. You need to visualise the plan and label the words from the given list (A-I).
Questions 11-15 Label the plan below.
Choose FIVE answers from the box and write the correct letters, A-I, next to questions 11-15A
.
Answers for sample 1
11. H
12. G
13. D
14. B
15. F
Sample 2
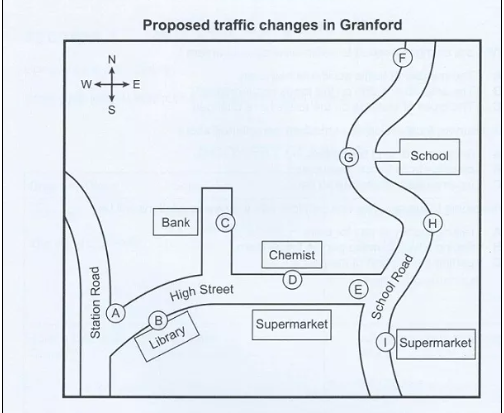
In sample 2, a recording of the chairman of the highways committee explaining the new traffic regulations and parking arrangements proposed for Granford at a public meeting is given. Here, you have to match the options from the letter A to I for the given questions.
Questions 14-20
Label the map below
Write the correct letter, A-I, next to questions 14-20.
14. New traffic lights .............
15. Pedestrian crossing ..............
16. Parking allowed ..............
17. New ‘No Parking’ sign ............
18. new disabled parking spaces ..........
19. Widened pavement ...........
20. Lorry loading/unloading restrictions ........
Answer for sample 2:
14. E
15. D
16. B
17. G
18. C
19. H
20. I
Sample 3
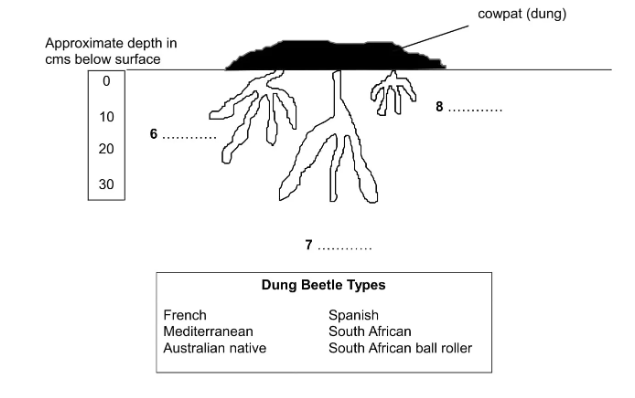
Sample 3 includes a list of words with which to label the diagram. The details required to label it correctly will be in the text; it may be given in paraphrasing and synonyms.
Questions 6-8
Label the tunnels on the diagram below using words from the box.
Write your answers in boxes 6-8 on your answer sheet.
Answers for sample 3
6. South African
7. French
8. Spanish
Sample 4
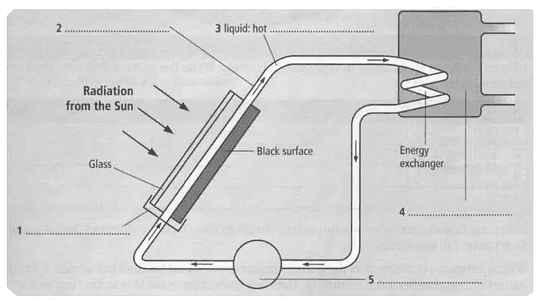
Sample 4 represents the diagram of a solar heating system and labels the parts given in the image from 1 to 5.
Questions 1-5
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.
Answers for sample 4
1. Solar panel
2. Copper pipe
3. Oil or water
4. Water tank
5. Pump
Sample 5
Label the diagram below.
Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer
Answers for sample 5
38. Holding tank
39. Slipstream
40. Coarse
Common Vocabulary: IELTS Listening Plan/Diagram Labelling
As of now, we have established the structure, sample tests and key components of the IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling questions. So to do well in this particular segment, you need to know the language of direction and location.
Vocabulary of Location
To be precise, vocabulary for location is where something is related to another object or place. Take a look below:
|
Vocabulary |
Meaning |
Examples |
|
In front of |
Just before or ahead of something |
The reception desk is in front of the entrance. |
|
opposite |
Facing something from across a space |
The cafe is opposite the library. |
|
adjacent to between |
Next to something or in the middle of two points |
The kitchen is adjacent to the dining room; the park is between the school and the hospital. |
|
across from |
On the other side of something, facing it. |
The bus stop is across from the supermarket. |
|
near |
Close to something |
The post office is near the train station. |
|
next to |
Immediately beside something |
The printer is next to the computer. |
|
beside |
At the side of something |
The garden is beside the house. |
|
at the corner |
Located where two edges meet |
The pharmacy is at the corner of Main Street and First Avenue. |
|
facing |
Located to look towards something |
The hotel is facing the beach. |
|
behind |
At the back of something |
The parking lot is behind the building. |
|
at the top |
Located at the uppermost part |
The logo is at the top of the page. |
|
at the bottom |
Located at the lowermost part |
The instructions are at the bottom of the page. |
|
in the middle |
Positioned at the centre between two points |
The fountain is in the middle of the square. |
|
below |
Directly lower than something |
The basement is below the ground floor. |
|
above |
Directly lower than something |
The balcony is above the entrance. |
|
underneath |
Directly beneath something |
The cat is sleeping underneath the table. |
|
on the left/right side |
Positioned to the left or right |
The library is on the left side of the street. |
|
in the centre |
Exactly in the middle of an area |
The statue is in the centre of the garden. |
|
inside/outside |
Within something / beyond its boundary |
The books are inside the cupboard; the garden is outside the house. |
|
attached to |
Connected or joined to something |
The shed is attached to the garage. |
|
on the edge |
Positioned at the boundary or border |
The bench is on the edge of the lake. |
Vocabulary of Directions
Directional vocabulary shows the position towards which someone moves or faces. Below are the common directional words with their application-based examples, which you can learn during IELTS exam preparation for high scores :
|
Vocabulary |
Meaning |
Examples |
|
Go straight on |
Continue moving forward without turning |
Go straight on for 200 meters, then you’ll see the library. |
|
turn left |
Change direction to the left |
Turn left at the traffic lights to reach the supermarket. |
|
turn right |
Change direction to the right |
Turn right at the corner to enter the park. |
|
go past (landmark/building) |
Use a specific street or road |
Go past the post office, and the bank will be on your left. |
|
take (street name) |
Use a specific street or road |
Take Oxford Street and walk until the square. |
|
take the (first/second/third street) on the right/left. |
Choose a street at a specific position in a sequence |
Take the second street on the left after the school. |
Tips to Solve IELTS Listening Plan/Diagram Labelling
Below are the key IELTS listening diagram labelling tips to follow for maximum score:
1. Thoroughwith Instructions
Read the instructions very clearly, because words and what you specifically need to do vary in this IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling questions.
For instance, the instructions for the first sample state: “Write the correct letter, A-I, next to Questions 14-20”.
So your job is to write a letter next to each word in the response list.
2. Read the Title & Labels
Do not limit yourself while learning about plan or diagram labelling from the existing labels and words. Sometimes, a diagram will also have a title that gives another big clue with respect to what the recording is about.
The more familiar you are with the vocabulary and the layout of the graphic, the easier it will be to follow the speaker's words.
3. Visualisation
We use plans and diagrams in everyday life due to one reason or another, so your brain is already used to doing this. So all you need to do is successfully visualise what the place described looks like.
How? Just imagine that you are standing in the location represented on the graphic and what you can see around you!
4. Synonyms & Paraphrasing
To solve the plan and labelling question accurately, you need to listen out for the synonyms and paraphrasing. As you are listening to the audio, remind yourself that you are not aiming for exact words in the task, but rather a similar meaning or context.
For example: If the answer is ‘reference books’, the audio might say instead:
- next to the history section
- dictionaries
- directories
- in the corner
- encyclopedias
5. Avoid Distractors
The examiners may trap you with the smart application of distractors. With this, the original piece of information changes and gives you a false illusion.
Ideally, ‘But’ and ‘However’ are particularly common distractors, but there are many other words and phrases that are as well.
For Example:
- The shop next to the bakery was a newsagent's, but it’s now been replaced by a charity shop.
- In the original design, the café and church were next to each other. However, the plans were changed to locate the church by the exit.
6. Mindful Guessing
If you miss any answer, take an intelligent guess, as this gives you the probability of getting it right. Well, this ability will develop while solving the IELTS listening practice test during preparation. This gives you some probability of getting it right.
7. Practice
Lastly, you should give more time to practice with an authentic IELTS listening mock test using the above tips and approach. As they give you a real exam simulation and you learn how to answer, common traps and distractors are used.
Master the IELTS exam with our Prep Boost
What’s included:
- Pre-recorded video lectures
- Advance Study Materials
- Detailed Feedback Report
Final Thought
As of now, you are clear about what exactly the IELTS listening plan and diagram labelling questions demand! Command over orientation and directional/ location vocabulary makes you the master in this section for sure. Along the way, our above-mentioned IELTS listening diagram labelling practice test will minimise the remaining loopholes in your preparation and give you the exam day confidence. You can even strengthen your preparation by taking our IELTS online coaching at Gradding.com, and make the most of the tricky questions into a wonderful opportunity and come with flying colours in the IELTS exam result.
FAQs
1. What is theDifference Between IELTS Plan and Diagram Labelling Questions?
The IELTS plan questions expect you to describe steps, sequence or processes. Whereas diagram labelling questions stresses on identifying and naming parts of a diagram without explaining the whole process.
2. Which Section of the IELTS Listening Test Includes Plan and Diagram Labelling?
Section 2 or Section 4 of the IELTS listening test usually contains plan and diagram labelling types of questions.
The possible reasons are:
- Section 2 contains a monologue about a place, map, or process, and the speaker describes locations or directions step by step.
- Section 4 comprises an academic monologue describing a process or diagram. And the speakers explain the parts of a process or system in order.
3. What Vocabulary is Important For Diagram Labelling?
Below are the important diagram labelling vocabulary in the IELTS listening section for reference:
- Prepositions: Above, below, next to.
- Linking words: First, then, finally.
- Nouns for parts.
- Verbs for processes.
- Adjectives describing positions or sizes.
4. What Skills are Tested in Plan and Diagram Labelling Questions?
Plan and diagram labelling questions evaluates following skills of test takers:
- Listening carefully
- Spatial relationships
- Following sequences
- Identifying key information
- Recognizing synonymous
- Interpreting descriptions
- Answer with precision.
5. How Can I Improve My Score in IELTS Listening Labelling Questions?
You can improve IELTS listening labelling questions thoroughly:
- Practice map
- Through with position vocabulary
- Anticipate answer
- Follow order
- Avoid spelling mistakes
0 comments

Practice Makes a Man Perfect!Take FREE ielts Mock Tests
Start FREE Mock TestPredict your IELTS Band

98% students got exact IELTS Band
What is your Target IELTS Band?
Get familiar with the Real IELTS Exam for Free!
Start Free Mock TestWe are available in :
BangaloreAhmedabadJaipurHyderabadKeralaPuneChandigarhMumbaiGurgaonChennaiKolkataTrivandrumNoidaKochiCalicutKottayamKollamThrissurIndoreUdaipurdisclaimer:logos and other registered trademarks of universities used on this platform are held by their respective owners. Gradding does not claim ownership or association on them, and their use is purely for informational and illustrative purposes.










